Emulsion cold mix asphalt plant
Asphalt Emulsion Cold Mix Manufacture
Classification as a function of coated material use
The name “cold mix” applies to three types of products which may be defined as follows:
* cold mixes for maintenance and small repair works in pavements,
* cold mixes for special uses (especially for floors in sports centres),
* cold mixes for pavement wearing courses.
Classification
Emulsión cold mixes may be classified as a function of their:
* use
* composition
* storability
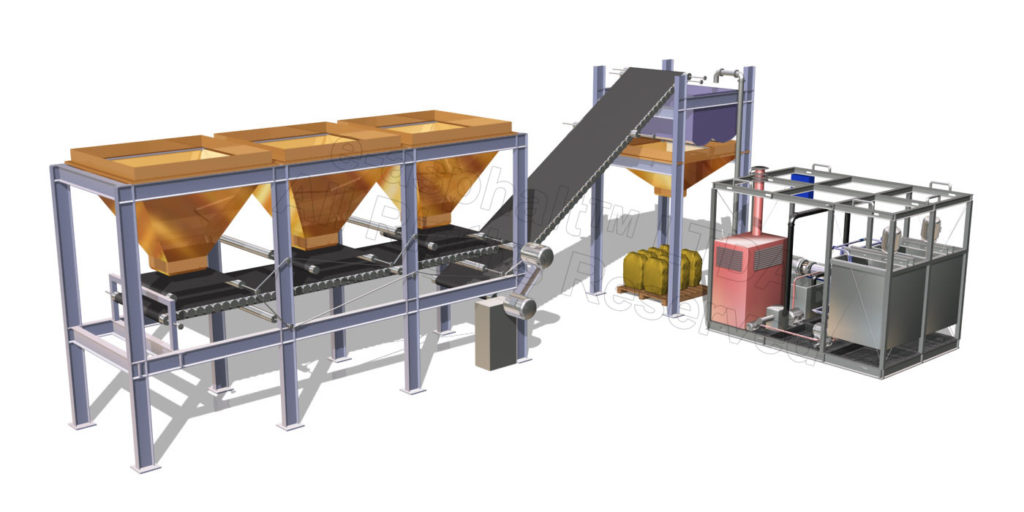

The two following manufacturing processes are available to make these three types of cold mixes:
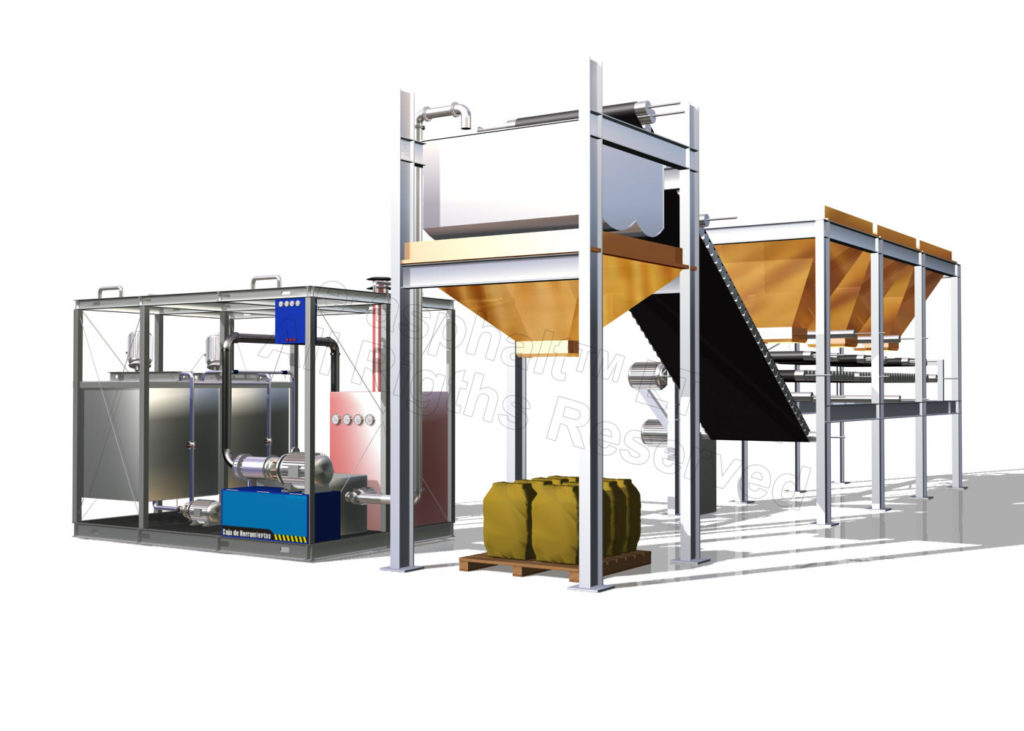

Stationary mixing plant
Cold mix, manufactured in a stationary plant, is normally intended for future use (from several hours to one month).
On-site manufacture
The cold mixes are manufactured and used immediately.
Classification as a function of coated material composition
Open graded cold mixes (O.F.D.)
Open graded cold mixes are manufactured from one of the following aggregate sizes: 2/4, 4/6, 6/10, 10/14, 10/20. A blend of aggregates from several sizes is sometimes used. The percentage of voids in these mixes is greater than 15%.
Semi-dense graded cold mixes (S.F.D.)
Semi-dense graded cold mixes are manufactured with 0/4, 0/6, 0/10 or 0/14 aggregates. The percentage of voids is between 10 and 15%.
Dense graded cold mixes (D.F.D.)
Dense graded cold mixes are manufactured with the same type of aggregates as semi-dense graded cold mixes but their filler content is higher. The percentage of voids is less than 10%. As the coating emulsion has a pure bitumen base, the storage time for these mixes is very low.
Classification as a function of mix storability
Storable cold mixes
Storable cold mixes or cold mixes for future use (from one hour to one month) are manufactured in a mixing plant with a continuous or discontinuous mix of one of the following types:
* mixer with a capacity of approximately 100 tons per day.
* discontinuous mixer, whose capacity is approximately 200 to 800 tons per day.
* continuous mixer, whose capacity is greater than 500 tons per day.
The source of aggregates depends on the use of cold asphalt: materials may be calcareous, silico-calcareous or from solid rock.
Aggregates are made entirely of crushed materials. The emulsión used has generally a cutback or fluxed bitumen base.
The percentage of flux depends on the end use of the cold asphalt, the laying equipment and the required storage lite. The residual binder content is a maximum of 5.5%. In the mixing plant, the aggregates are supplied from separate weigh hoppers, making it possible to produce the required grading by adjusting the supply rates. The binder is stored in a tank and is injected into the mixer by means of a metering pump. Product delivery to the customer is in bulk by tipper trucks or in easy to use small packages (bags or drums) for small repair works. The product may be bulk coloured. Laying is by hand, or with a grader or a paver.
Immediate use or non-storable cold mixes
These asphalts are manufactured on site in a mobile mixing plant. This plant consists of a coating truck when the site work mainly consists of repairs. In this case, laying is by hand. The aggregate fed to the mixer is graded at the quarry. When the cold asphait is for a wearing course, the plant is of the motopaver type. A mixer fitted with dosing pumps is used to manufacture the cold asphalt with the required residual bitumen and water content. Contents are selected to provide the required mechanical performances and to facilitate work. The aggregate fed to the mixer is graded at the quarry site.
The emulsion used is based on a pure bitumen which gives the asphalt high mechanical properties as soon as the breaking water is expelled.
Laying is by means of:
* either a grader; when the asphalt is previously placed in calibrated windrows,
* or by means of a vibrating table, similar to that in a paver, which spreads the cold mix and, at the same time, compacts it at the outlet from the machine.


